Do you immediately clean your Teeth after eating? If not, you may see your teeth getting covered in a thin, sticky film. This accumulation, which covers many teeth and begins to fill up gaps, is known as a Calculus bridge. Gum disease and tooth decay are two primary dental conditions that may result from this if left untreated.
An overview of calculus bridges, including their origins, effects on dental health, and preventative and treatment options, is given in this article.
A Calculus Bridge: What Is It?
Dental calculus, often known as tartar, appears as a white or yellowish buildup of minerals on the surfaces of teeth. Curiously, calculus mainly develops in regions near the mouth cavity’s entrance where salivary gland ducts discharge.
The calcified plaques are the source of this hard deposit. The development of calculus differs from person to person and is impacted by components found in saliva, calcium concentration, and pH level. If left untreated, the calculus can worsen and develop into a bridge that crosses the gum line, the spaces between teeth, and even more teeth. This endangers dental health in addition to impairing oral attractiveness.
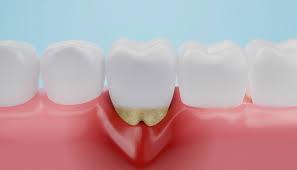
What Does a Calculus Bridge Look Like?
In contrast to plaque, calculus buildups are visible and can have different colors depending on how close they are to the gum line. Denser and clay-like, calculus is usually yellow above the gum line and dark brown, green, or black underneath it.
A calculus bridge is created when calculus covers many teeth in a row and fills up the spaces between them. Although every instance is different, a calculus bridge often begins as a dark stain along the gum line and then spreads to other parts of the teeth.
How is calculus removed?
Calculus must be eliminated since it is rife with microorganisms. Tartar removal can only be accomplished by seeing a dentist. Your dental hygienist can use specialized equipment and an ultrasonic tool to remove the stubborn build-up. Regular cleaning is an effective procedure to eliminate a calculus bridge since it forms above the gumline. Due to the irritation caused by the tartar, the gums may be a little sensitive after cleaning, but they will recover when the tartar is removed. Make an appointment at least twice a year or three or four times if you are a quick learner of calculus.
Effects of Using a Calculus Bridge
Following are the major effects of Using a Calculus Bridge
Bad breath or halitosis
Bacteria and plaque accumulation can cause an odor in your mouth and breath.
Gingival inflammation
Gum inflammation, which results in red gums, is a possible side effect of the ailment often known as gum disease. The first thing you could notice is bleeding when you brush or floss. Gingivitis can worsen and develop into periodontitis if left untreated.
Receding gums
More of your teeth may become visible when your gums start to recede from them. This makes it easier for the germs to enter the spaces between your teeth and gums.
Cavities
The germs may be shielded from the toothbrush by the calculus or tartar layer. Additionally, tartar can lead to the development of tiny holes in the enamel, which opens the door for bacteria and acid to enter the tooth and create cavities.
Source
Preventing the buildup of calculus
Maintaining good oral hygiene is essential to avoiding calculus development. The American Dental Association has the following advice for preventing calculus:
- Use fluoride toothpaste twice a day to brush your teeth. To allow yourself enough time to brush every surface of every tooth, make sure you spend at least two full minutes brushing each time.
- Every day, floss. Because plaque remains in the spaces between your teeth, brushing only eliminates 40% of the tartar on your teeth. The only way to get rid of this is to floss. Flossing is better for cleaning the spaces between teeth and beneath the gum line.
- Limit your consumption of sugary foods and beverages: Reducing your sugar intake helps to decrease the chances that oral bacteria will interact with sugar residues and cause plaque to build on your teeth.
- Maintain routine dental appointments. A dentist will keep a close eye on your gums and teeth to look for indications of gum disease, tooth decay, gingivitis, and receding gums. This enables them to address these problems before they become out of control.
- See your dentist regularly to avoid excessive tartar accumulation.
Techniques to Prevent the Formation of Calculus Bridges:
Here’s how to strengthen your resistance against it
Frequent Brushing:
Make it a point to use a soft-bristled toothbrush to clean your teeth twice daily. Use a circular motion to guarantee thorough cleaning without putting undue strain on the enamel or irritating the gums.
Daily Flossing:
Flossing aids in the removal of food particles and plaque that brushing may miss from between teeth.
Rinses with fluoride:
Include a fluoride rinse in your routine according to your dentist’s advice. This strengthens the teeth against decay in addition to fighting bacteria.
Maintain Hydration:
During the day, sip plenty of water. This easy action helps wash away residual germs, lowering the likelihood that plaque will develop.
Pay Attention to Your Diet:
Not only are processed meals, chocolates, and sweets bad for your general health, but they also hasten plaque buildup. Eat them in small amounts.
Natural Assistance:
Use natural therapies such as orange peel as a substitute measure. Its vitamin C concentration helps fight germs in the mouth. You may use fresh orange peels as an additional cleaning method by gently rubbing them on your teeth for a few minutes daily.
Appropriate Dental Visits:
Frequent dental examinations are essential. Make an appointment when you notice recession, redness in your gums, or any signs of tartar accumulation. Further issues can be avoided with early identification and action.
Conclusion
Dental calculus bridges indicate poor dental hygiene and are typically caused by tartar accumulation. Its growth can be considerably aided by elements like smoking, eating an unhealthy diet, and not practicing good oral care. If left untreated, this illness can lead to more severe issues, including gingivitis, foul breath, receding gums, and sometimes even tooth loss.
Also Read : Reveal the Mystery About Abigail Breslin Teeth