Highlights
- Normally functioning erectile tissue fills with arterial blood, helping the penis to become erect.
- Erectile tissue can be damaged suddenly due to penile injury or over time by chronic conditions and other issues.
- Common symptoms of penile damage include difficulty with erections, changes in the shape of the penis, and pain with erection or ejaculation.
- Erectile tissue damage needs to be diagnosed and treated as quickly as possible to preserve your sexual health.
- Knowing the signs and common causes of erectile tissue damage can help you decide when to contact a doctor.
Your Erectile Tissue is key to your penile health, yet most men aren’t familiar with the signs of erectile tissue damage and the risk leaving it untreated can have on your sex life. Learn what erectile tissue damage is, why it’s a problem, effective treatment, answers to your questions, and when to see a doctor.
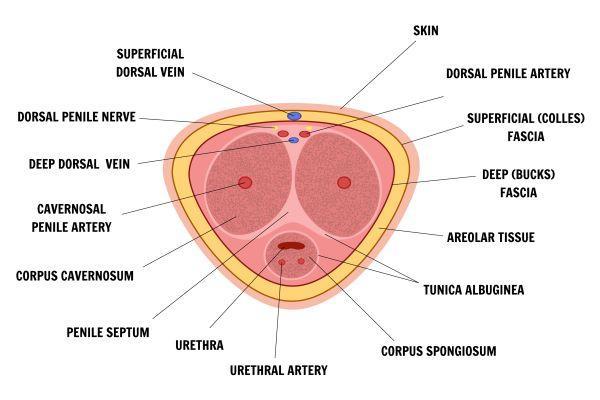
What Is Erectile Tissue?
Your erections depend on healthy erectile tissue, yet many men don’t understand what it is and how easily it can be damaged.
Erectile tissue is a specialized type of spongy tissue found primarily within the penis (though you also have it in your nose). It consists of a complex network of blood vessels and smooth muscle fibers that are arranged in cavernous spaces.
Here’s how it functions:
At rest: In its flaccid state, the smooth muscles within erectile tissue remain contracted, restricting blood flow. Only a minimal amount of blood circulates, just enough for basic tissue maintenance.
Arousal: When you’re sexually stimulated, a series of neural and hormonal signals trigger the relaxation of the smooth muscles in the erectile tissue. This allows the cavernous spaces to expand.
Engorgement: As the spaces expand, there’s a dramatic increase in blood flow into the penis. This blood becomes trapped within the erectile tissue, causing it to swell and the penis to become firm.
After ejaculation: The excitement fades, and signals cause the smooth muscles to contract again. The excess blood gradually drains from the erectile tissue, returning the penis to its flaccid state.
What Causes Erectile Tissue Damage?
Your erections depend upon healthy erectile tissue, but a number of things can damage that tissue, including:
- Injury to the penis. Both sudden erectile tissue injury and injury over time, such as sports injuries, can cause damage.
- Medical conditions. Diabetes, high blood pressure, and other vascular conditions cut blood supply to your erectile tissue, depriving it of nutrients and oxygen.
- Medication. A wide range of medications can affect sexual performance for different reasons. For any medication that cites erectile dysfunction (ED) as a possible side effect, check on tissue damage risk with your doctor.
- Lifestyle. Smoking, limited exercise, poor diet, and other lifestyle factors contribute to chronic conditions that can contribute to erectile tissue damage and possibly cause damage directly as well.
The most well-known form of tissue damage is penile fracture, where the tunica albuginea is snapped due to the penis being bent or otherwise experiencing significant force while erect, most often during sex. Penile fracture is rare, however — long-term damage is more likely.
5 Signs of Erectile Tissue Damage
While erectile tissue can heal if it has enough time and the body gets to it soon enough, damage can affect it over time. That’s why familiarity with the 5 warning signs of penile damage below is so important.
Here are the symptoms you should not ignore.
1. Difficulty Achieving or Maintaining Erections
A common sign is an increasing difficulty in getting and keeping an erection, absent any other known cause. While this can happen to any man once in a while, if it’s a consistent issue, that should be a point of concern.
But remember that erectile dysfunction can have a wide range of causes, and ED itself isn’t a sign of erectile tissue damage. However, many other root causes of ED are serious medical conditions that should be checked out.
2. Reduced Erectile Function Over Time
While some loss of erectile function is expected as a normal part of aging, what you’re looking for is a noticeable loss of function over a relatively short time. For example, if you’re diagnosed with a chronic condition and have had problems in the bedroom before, you might notice that they become more intense over time.
This can be difficult to measure, in part because other causes of ED can also make themselves known over time. For example, somebody with ED due to depression might notice their ED gradually getting worse as they work to manage their depressive episodes. It can also be difficult to track unless you’re taking careful notes.
Talk with your partner and ask them if they’ve noticed anything. And even if it’s only a hunch, it’s worth following with a medical professional.
3. Pain During Erection or Ejaculation
Pain while becoming erect or ejaculating is fairly rare, and a point of concern regardless of the cause. With erectile tissue, the damage can be due to strain on the tissues or poor healing, similar to how a poorly set broken bone will feel painful in certain conditions.
If the pain is ongoing and consistent, every time you get an erection, or severe enough that it interferes with your sex life, consider it a warning sign.
4. Changes in the Shape of the Penis
One of the more noticeable signs of tissue damage is changes in shape. The most famous example of this is Peyronie’s disease, where scar tissue builds up on the penis and causes it to bend or distort. Some men also notice indentations or other unusual changes. These plaques of scar tissue can be felt under the skin and are sometimes painful as well.
Just how common these problems are is up for debate. One study of American men found that 0.7% had Peyronie’s disease, but a further 11% of men may have had it based on how they answered survey questions but were never diagnosed. Even if you don’t have other concerns, treating Peyronie’s has become easier and it’s worth getting informed.
5. Swelling or Lumps in the Penis
Like any damaged tissue, erectile tissue will become inflamed when damaged, leading to swelling. Lumps can also form as scar tissue as it tries to heal. Like Peyronie’s plaques, you’ll be able to feel these lumps under the skin.
Preventing and Treating Erectile Tissue Damage
Preserving your erectile tissue is all about planning ahead. Here’s how.
- Keep up a healthy lifestyle. A healthy diet, regular exercise, limiting alcohol, and quitting smoking all support your overall health and reduce the risk to erectile tissue.
- Protect yourself. When playing sports or otherwise being active, use protective gear such as an athletic supporter if there’s a risk of erectile tissue injury.
- Manage medical conditions. Follow the care regimen prescribed by your doctor for chronic conditions and other issues.
- Get regular check-ups. Standard preventative care helps you catch problems before they come up.
If you do have erectile tissue damage, there are some treatment options. Surgery to remove the scar tissue can help with function and reduce pain and discomfort. In addition to ED medication, an enzyme that breaks down collagen can be injected into scar tissue to break it down, currently sold under the brand name Xiaflex.
Don’t Sleep on Erectile Tissue Damage
Whether it happens suddenly or over time, erectile tissue damage needs to be caught and treated as early as possible. The earlier you’re diagnosed, the sooner you can start getting treatment, whether it’s for the root causes or for the side effects of tissue damage.
Below you’ll find the answers to frequently asked questions about penile health. Don’t forget, however, that a doctor is your best option for both diagnosis and treatment.
Frequently Asked Questions about Erectile Tissue Damage
Is erectile tissue damage the same as erectile dysfunction?
Erectile tissue damage is a possible cause of erectile dysfunction, but they’re not the same. Erectile dysfunction can have a variety of causes and even be caused by multiple issues at once, including cardiovascular problems, hormone imbalances, and psychological conditions.
How do I know if I’ve damaged my erectile tissue?
In addition to the signs listed above, look for the following:
- A popping sound, possibly followed by a sudden loss of erection
- Tingling or other uncomfortable sensations
- Blood from the urethra
- Difficulty urinating
- Bruising or discoloration
- Softer or painful erections
If you’re experiencing any of these, see a medical professional right away.
Are there ways to prevent erectile tissue damage?
Prevent injury by wearing protective clothing during sports and other situations where you might experience a groin injury, and be careful in certain sexual positions where you can suddenly bend or warp your penis. Contrary to popular myth, the missionary position was found to have the highest risk, followed by “doggy style,” according to one study. Partner-on-top showed relatively low risk.
For other forms of damage, make key lifestyle changes. Quitting smoking, getting exercise, and improving your diet will all protect your erectile tissue and your overall health as well.
Can erectile tissue damage heal on its own?
Like most tissue, erectile tissue can heal on its own, depending on the severity of the injury. However, much as you wouldn’t allow a bone fracture to “just heal,” leaving erectile tissue to heal on its own can lead to complications down the road. If you think you’ve damaged your erectile tissue, see a doctor.
Will I be able to have sex again after erectile tissue damage?
Yes! Once you’re fully healed and in the absence of any complications, you should be able to return to a normal sex life.
Is it normal to have pain after a penile injury?
Yes. However, if the pain is consistent whenever you get an erection or doesn’t go away after the initial injury, get checked out immediately.
Are there non-surgical options for treating erectile tissue damage?
Non-surgical options will depend on the extent of the damage and the cause. Lifestyle changes and managing chronic conditions limits tissue damage over time. Sudden breaks caused by pressure or force put on the penis, though, almost always need surgery.
How long does it take to recover from penile injury?
Recovery times depend heavily on factors like your overall health, the severity of the injury, and interventions.
What are the long-term symptoms of penile fracture?
Long-term symptoms of penile damage can include:
- Peyronie’s disease
- Loss of sexual function
- Difficulty in getting an erection
- Pain when having an erection or during sex
- Erectile dysfunction
These conditions can all have other causes as well, so a check-up is in order if you’re experiencing them.
What is the treatment for penile fracture?
Penile fracture is usually treated with surgery. Older, healed breaks may be treated with medication like Xiaflex.
Can erectile function be restored after penile fracture?
Yes. In fact, it’s recommended to receive surgery as quickly as possible to maintain sexual function.
Can a penile fracture cause emotional distress?
Yes. Penile fracture is often painful and can be tied to how you feel about your masculinity. If you find yourself obsessing over the incident or worrying it’ll happen again, speak with a mental health professional.
Don’t Let Erectile Tissue Damage Hold You Back
Erectile tissue damage can be limited if you take the right steps. First, make an appointment with your doctor and talk about your possible risks and how to manage them. Then, take those steps to keep your penis, and yourself, in better shape.
eDrugstore helps by giving you options for managing your erectile health. Our free telehealth services and evidence-based health information help you make informed decisions about ED and your overall health.
To learn more about ED and treating it with prescription medication, visit our erectile dysfunction page.
Disclaimer: This article provides general information about health and related topics but is not intended as a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of your physician or other qualified health provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition.
The post 5 Signs of Erectile Tissue Damage You Should Not Ignore (+ FAQ) first appeared on Online Prescription Medications.This post first appeared on Edrugstore.com Blog | Current Health News, please read the originial post: here