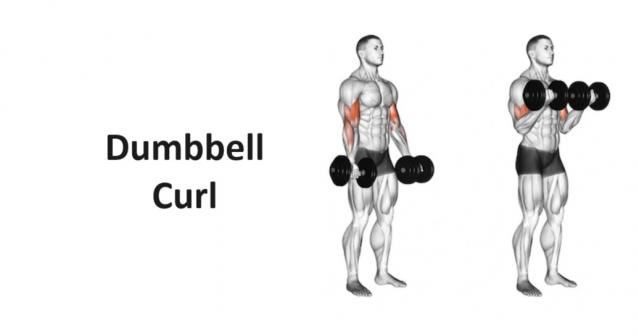
The Dumbbell Curl is a fundamental strength training exercise that primarily targets the biceps muscles. It is a simple yet effective movement that can be performed using a pair of dumbbells, making it accessible to individuals of all fitness levels. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the correct technique, benefits, variations, and other essential details associated with the Dumbbell Curl.
Instructions
Setup:
- Select Dumbbells: Choose a pair of dumbbells that allow you to perform the exercise with proper form and control. Start with lighter weights if you’re new to the exercise and gradually increase the resistance as you become stronger.
- Standing Position: Stand tall with your feet shoulder-width apart, knees slightly bent, and core engaged. Hold a dumbbell in each hand, arms fully extended by your sides, palms facing forward.
Execution:
- Starting Position: Keep your upper arms stationary and your elbows close to your sides throughout the exercise. Maintain a neutral spine and avoid excessive swinging or leaning.
- Curling Motion: Exhale as you flex your elbows and curl the dumbbells towards your shoulders in a controlled manner. Keep your wrists straight and focus on contracting your biceps muscles throughout the movement.
- Peak Contraction: Once the dumbbells reach shoulder level or slightly higher, pause for a brief moment to squeeze your biceps at the top of the movement. This maximizes muscle activation and helps develop muscle definition.
- Lowering Phase: Inhale as you slowly lower the dumbbells back to the starting position, maintaining control over the descent. Avoid letting the weights drop quickly or using momentum to lift the weight.
- Repeat: Perform the desired number of repetitions with proper form and control. Aim for a full range of motion, allowing the dumbbells to fully extend at the bottom of each repetition.
Tips:
- Focus on a slow and controlled tempo, emphasizing the eccentric (lowering) phase of the movement to maximize muscle activation.
- Keep your shoulders back and chest up throughout the exercise to maintain proper posture and prevent excessive swinging.
- Avoid using momentum or swinging the dumbbells to lift the weight. Concentrate on using your biceps muscles to perform the movement.
Benefits
- Biceps Development: The Dumbbell Curl is highly effective for targeting the biceps muscles, leading to increased strength, size, and definition in the arms.
- Stability and Balance: Performing the exercise with dumbbells requires greater stabilization and balance compared to barbell or machine variations. This can help improve overall coordination and stability in the upper body.
- Versatility: Dumbbells allow for a wide range of motion and variations, making the exercise adaptable to individual preferences and fitness goals. You can perform the Dumbbell Curl in various positions, such as seated, standing, or incline.
- Unilateral Training: Performing the exercise with dumbbells allows for unilateral training, meaning you can work each arm independently. This helps address muscle imbalances and ensures balanced development between the left and right sides of the body.
Muscles worked in Dumbbell Curl
The Dumbbell Curl primarily targets the biceps brachii muscles, which are located on the front of the upper arm. However, several other muscles are also involved in supporting and stabilizing the movement. Here are the main muscles worked during the Dumbbell Curl:
- Biceps Brachii: As the primary mover in the exercise, the biceps brachii muscles are heavily engaged during the Dumbbell Curl. They are responsible for flexing the elbow joint and bringing the hand towards the shoulder.
- Brachialis: The brachialis muscle lies underneath the biceps brachii and plays a significant role in elbow flexion. It is activated to a lesser extent compared to the biceps brachii but still contributes to the overall strength and size of the upper arm.
- Brachioradialis: The brachioradialis muscle is located on the forearm and assists in elbow flexion. It is activated during the Dumbbell Curl, especially when using heavier weights or when the forearm is in a neutral position.
- Forearm Muscles: The muscles of the forearm, including the flexor muscles, are involved in maintaining grip on the dumbbells and stabilizing the wrist joint during the curling motion. They provide support and stability throughout the exercise.
Overall, the Dumbbell Curl is an effective exercise for targeting the muscles of the upper arm, particularly the biceps brachii, while also engaging other supporting muscles to provide stability and control. By performing the exercise with proper form and technique, you can effectively develop strength, size, and definition in the biceps.
Alternate names for Dumbbell Curl:
- Bicep Curl
- Dumbbell Bicep Curl
- Arm Curl
- Dumbbell Arm Curl
Variations
- Alternating Dumbbell Curl: Alternate curling each arm while the other arm remains stationary. This variation allows for continuous tension on the biceps and can increase the intensity of the exercise.
- Hammer Curl: Perform the curling motion with your palms facing each other (neutral grip) instead of facing up. This variation targets the brachialis and brachioradialis muscles to a greater extent.
- Seated Dumbbell Curl: Perform the exercise while seated on a bench to minimize momentum and isolate the biceps muscles further.
Conclusion
The Dumbbell Curl is a versatile and effective exercise for targeting the biceps muscles. By mastering the correct technique, incorporating variations, and progressively overloading the muscles, you can achieve impressive results in biceps development and overall upper body strength.