Scalability Testing is a type of performance testing that evaluates a system’s ability to handle increasing workloads and maintain performance as the workload grows. It assesses how well a system can scale up or scale out to accommodate growing user demands and data volumes while maintaining acceptable performance levels.
1. Importance of Scalability Testing:
- Business Growth: Ensures that systems can accommodate increased user traffic and data volume resulting from business growth.
- User Satisfaction: Prevents performance degradation and ensures a seamless user experience even during peak usage periods.
- Cost Efficiency: Identifies potential scalability issues early in the development lifecycle, reducing the cost of addressing them later.
2. Types of Scalability Testing:
- Vertical Scalability Testing: Assess the system’s ability to handle increased workload by adding more resources to a single server (scaling up).
- Horizontal Scalability Testing: Evaluate the system’s ability to distribute workload across multiple servers or nodes in a distributed environment (scaling out).
3. Key Components of Scalability Testing:
- Load Testing: Simulate user interactions and measure system performance under increasing load levels to identify performance bottlenecks.
- Stress Testing: Push the system beyond its intended capacity to determine its breaking point and measure how it recovers from failure.
- Capacity Testing: Determine the maximum capacity of the system in terms of users, transactions, or data volume it can handle without degradation.
- Elasticity Testing: Evaluate how well the system can dynamically scale resources up or down based on fluctuating demand.
4. Best Practices for Scalability Testing:
- Realistic Workloads: Use realistic usage scenarios and data sets to simulate actual user behavior and workload patterns.
- Incremental Testing: Start with small-scale tests and gradually increase the workload to identify performance thresholds and scalability limits.
- Automated Testing: Implement automated testing frameworks and tools to streamline scalability testing and ensure repeatability.
- Monitoring and Analysis: Continuously monitor system performance metrics during testing and analyze results to identify performance bottlenecks and scalability issues.
- Failure Recovery Testing: Evaluate the system’s ability to recover from failures gracefully and maintain acceptable performance levels during and after failure scenarios.
5. Benefits of Scalability Testing:
- Improved Performance: Ensures that systems can handle increased workload without degradation in performance or response times.
- Enhanced Reliability: Identifies scalability issues early, allowing for proactive optimization and mitigation measures to improve system reliability.
- Cost Savings: Helps avoid costly downtime and performance-related issues by addressing scalability issues before they impact users or business operations.
6. Key Takeaways:
- Scalability testing evaluates a system’s ability to handle increased workload and maintain performance as the workload grows.
- It includes load testing, stress testing, capacity testing, and elasticity testing to assess various aspects of scalability.
- Scalability testing is essential for ensuring optimal performance, reliability, and cost efficiency of systems in dynamic and growing environments.
Connected Agile & Lean Frameworks
AIOps
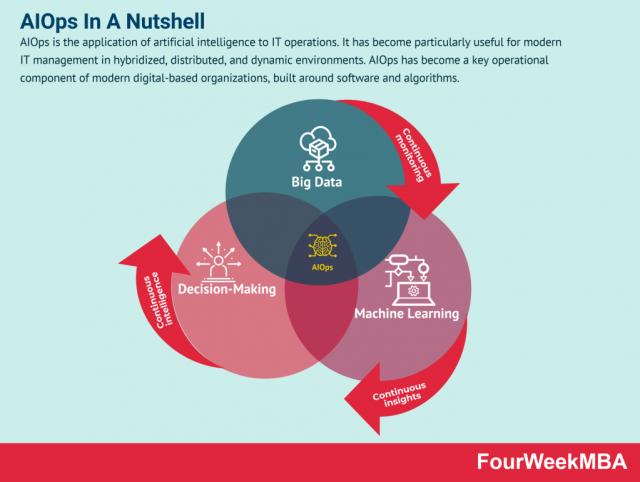
AIOps is the application of artificial intelligence to IT operations. It has become particularly useful for modern IT management in hybridized, distributed, and dynamic environments. AIOps has become a key operational component of modern digital-based organizations, built around software and algorithms.
AgileSHIFT
AgileSHIFT is a framework that prepares individuals for transformational change by creating a culture of agility.
Agile Methodology
Agile started as a lightweight development method compared to heavyweight software development, which is the core paradigm of the previous decades of software development. By 2001 the Manifesto for Agile Software Development was born as a set of principles that defined the new paradigm for software development as a continuous iteration. This would also influence the way of doing business.
Agile Program Management
Agile Program Management is a means of managing, planning, and coordinating interrelated work in such a way that value delivery is emphasized for all key stakeholders. Agile Program Management (AgilePgM) is a disciplined yet flexible agile approach to managing transformational change within an organization.
Agile Project Management
Agile project management (APM) is a strategy that breaks large projects into smaller, more manageable tasks. In the APM methodology, each project is completed in small sections – often referred to as iterations. Each iteration is completed according to its project life cycle, beginning with the initial design and progressing to testing and then quality assurance.
Agile Modeling
Agile Modeling (AM) is a methodology for modeling and documenting software-based systems. Agile Modeling is critical to the rapid and continuous delivery of software. It is a collection of values, principles, and practices that guide effective, lightweight software modeling.
Agile Business Analysis
Agile Business Analysis (AgileBA) is certification in the form of guidance and training for business analysts seeking to work in agile environments. To support this shift, AgileBA also helps the business analyst relate Agile projects to a wider organizational mission or strategy. To ensure that analysts have the necessary skills and expertise, AgileBA certification was developed.
Agile Leadership
Agile leadership is the embodiment of agile manifesto principles by a manager or management team. Agile leadership impacts two important levels of a business. The structural level defines the roles, responsibilities, and key performance indicators. The behavioral level describes the actions leaders exhibit to others based on agile principles.
Andon System
The andon system alerts managerial, maintenance, or other staff of a production process problem. The alert itself can be activated manually with a button or pull cord, but it can also be activated automatically by production equipment. Most Andon boards utilize three colored lights similar to a traffic signal: green (no errors), yellow or amber (problem identified, or quality check needed), and red (production stopped due to unidentified issue).
Bimodal Portfolio Management
Bimodal Portfolio Management (BimodalPfM) helps an organization manage both agile and traditional portfolios concurrently. Bimodal Portfolio Management – sometimes referred to as bimodal development – was coined by research and advisory company Gartner. The firm argued that many agile organizations still needed to run some aspects of their operations using traditional delivery models.
Business Innovation Matrix
Business innovation is about creating new opportunities for an organization to reinvent its core offerings, revenue streams, and enhance the value proposition for existing or new customers, thus renewing its whole business model. Business innovation springs by understanding the structure of the market, thus adapting or anticipating those changes.
Business Model Innovation
Business model innovation is about increasing the success of an organization with existing products and technologies by crafting a compelling value proposition able to propel a new business model to scale up customers and create a lasting competitive advantage. And it all starts by mastering the key customers.
Constructive Disruption
A consumer brand company like Procter & Gamble (P&G) defines “Constructive Disruption” as: a willingness to change, adapt, and create new trends and technologies that will shape our industry for the future. According to P&G, it moves around four pillars: lean innovation, brand building, supply chain, and digitalization & data analytics.
Continuous Innovation
That is a process that requires a continuous feedback loop to develop a valuable product and build a viable business model. Continuous innovation is a mindset where products and services are designed and delivered to tune them around the customers’ problem and not the technical solution of its founders.
Design Sprint
A design sprint is a proven five-day process where critical business questions are answered through speedy design and prototyping, focusing on the end-user. A design sprint starts with a weekly challenge that should finish with a prototype, test at the end, and therefore a lesson learned to be iterated.
Design Thinking
Tim Brown, Executive Chair of IDEO, defined design thinking as “a human-centered approach to innovation that draws from the designer’s toolkit to integrate the needs of people, the possibilities of technology, and the requirements for business success.” Therefore, desirability, feasibility, and viability are balanced to solve critical problems.
DevOps
DevOps refers to a series of practices performed to perform automated software development processes. It is a conjugation of the term “development” and “operations” to emphasize how functions integrate across IT teams. DevOps strategies promote seamless building, testing, and deployment of products. It aims to bridge a gap between development and operations teams to streamline the development altogether.
Dual Track Agile