MongoDB’s business model revolves around empowering developers through its integrated developer data platform, which offers a unique document-based architecture combining relational and non-relational Database strengths. By emphasizing the strategic importance of database selection and addressing challenges of legacy systems, Mongodb aims to support modern application requirements. With MongoDB Atlas simplifying database management and a focus on customer benefits like maximizing competitive advantage and reducing total cost of ownership, MongoDB drives growth through product innovation, fostering a vibrant developer community, expanding its partner ecosystem, and international expansion.
Key elements of MongoDB business model
- Mission: MongoDB aims to empower developers to innovate and disrupt industries by leveraging the power of software and data.
- Integrated Developer Data Platform: MongoDB offers an integrated set of database and related services to address modern application requirements with a unified and consistent user experience.
- Document-Based Architecture: Built on a unique document-based architecture, MongoDB’s database combines the strengths of relational and non-relational databases, offering performance, scalability, flexibility, and reliability.
- Strategic Importance of Database Selection: MongoDB emphasizes the strategic significance of selecting the right database, as it directly impacts developer productivity, application performance, and organizational competitiveness.
- Challenges of Legacy Relational Databases: Legacy relational databases are highlighted as inadequate for modern, agile software development due to their rigidity, lack of support for cloud deployments, and difficulty in handling large volumes of data.
- Generative AI and Database Requirements: The emergence of generative artificial intelligence (AI) underscores the need for modern databases to securely build, deploy, and scale AI-powered applications, leveraging proprietary data.
- Additional Platform Capabilities: MongoDB’s developer data platform includes capabilities such as search, vector search, time series, data lifecycle management, application-driven analytics, and edge computing, offering a comprehensive solution for diverse application requirements.
- Market Competitiveness and Growth: MongoDB competes in the database management software market, which is forecasted for significant growth. Developments in coding assistant technology are expected to further benefit the market.
- MongoDB Advantage: MongoDB’s key differentiating features include its developer-centric approach, support for modern applications, versatility, performance, scalability, flexibility, control, and reliability.
- Support for Any Application Anywhere: MongoDB enables customers to run applications across various environments, including fully managed as a service, self-managed in the cloud, on-premises, or in a hybrid environment, providing flexibility, optionality, and efficiency.
- MongoDB Atlas: MongoDB Atlas, the multi-cloud developer data platform offering, simplifies database management for organizations by providing MongoDB as a service in the public cloud, allowing developers to focus on application performance and user experience without worrying about infrastructure management.
MongoDB’s Developer Data Platform
- Maximize Competitive Advantage: MongoDB’s platform supports the development of modern applications, enabling organizations to leverage software and data effectively to gain a competitive edge. This leads to improved end-user satisfaction, increased revenue, and enhanced market share.
- Increase Developer Productivity: By offering tools and architecture that facilitate rapid application development and modernization, MongoDB enhances developer agility and accelerates time-to-market for new products. MongoDB Atlas further streamlines development by handling database infrastructure management tasks, allowing developers to focus on application performance and user experience.
- Deliver High Reliability: MongoDB’s platform is engineered to ensure high reliability for mission-critical deployments. Its fault-tolerant architecture and “always-on” design minimize downtime, reducing the risk of lost revenue for customers.
- Reduce Complexity: The integrated capabilities of MongoDB’s platform reduce the need for disparate solutions, simplifying the application infrastructure. This reduction in complexity leads to lower operational overhead and improved efficiency in managing modern applications.
- Reduce Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): MongoDB’s platform contributes to lowering the TCO for enterprises through several means. Firstly, it speeds up application development, reducing the resources required for maintenance. Secondly, it operates on commodity hardware and requires less management, leading to lower infrastructure costs. Lastly, it offers flexibility in deployment, enabling cost-effective cloud or alternative environments. Overall, these factors contribute to a significant reduction in application-related overhead costs and TCO for MongoDB customers.
MongoDB’s Products
- MongoDB Atlas: This managed multi-cloud Database-as-a-Service (DBaaS) offering provides comprehensive infrastructure and management, enabling customers to focus on application development rather than database management. It offers automated provisioning, healing, monitoring, backup, and security features across multiple cloud providers, facilitating flexibility and avoiding vendor lock-in.
- Features and Enhancements: MongoDB Atlas has evolved with additional features like Atlas Search, Atlas Device Sync, Atlas Data Federation, Atlas Charts, and recently introduced MongoDB Atlas Vector Search and MongoDB Atlas Stream Processing. These features enhance search capabilities, simplify AI application development, and enable real-time data processing, contributing to operational efficiency and innovation acceleration.
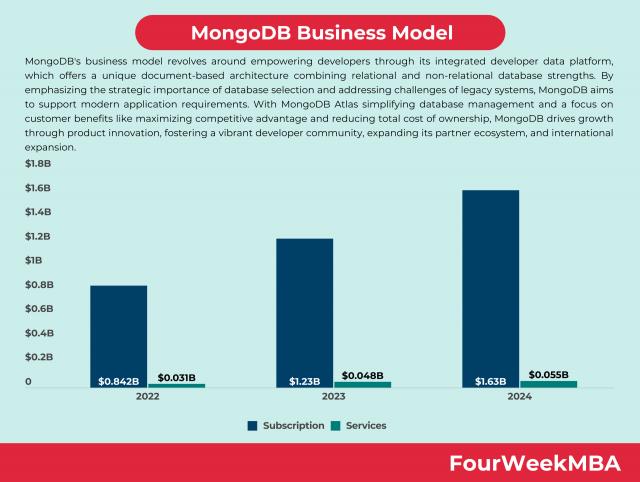
- Revenue Contribution: MongoDB Atlas has seen significant revenue growth, representing a substantial portion of MongoDB’s total revenue over the years, indicating its popularity and adoption by customers.
- MongoDB Enterprise Advanced: This self-managed commercial database offering targets enterprise customers and can run in various environments, including cloud, on-premises, or hybrid setups. It includes the MongoDB Enterprise Database Server, enterprise management capabilities via Cloud Manager Premium or Ops Manager, and analytics integrations to facilitate efficient data analysis.
- Professional Services: MongoDB offers professional services such as consulting and training to ensure successful customer deployments, driving customer retention and revenue expansion. These services complement the platform’s ease of deployment and contribute to faster adoption and increased usage by customers.
- Free Offerings: MongoDB provides Community Server and a free tier of MongoDB Atlas to encourage developer adoption. Community Server offers core functionality for developers, while the free tier of MongoDB Atlas allows limited access to the hosted database solution. These offerings serve as entry points for users, potentially converting them into paying customers of MongoDB’s commercial offerings.
- Intellectual Property and Business Model: MongoDB’s proprietary software subscription business model is supported by owning the intellectual property of its offerings. This ownership enables control over the product roadmap, including features included in free or paid offerings, ensuring alignment with business objectives and customer needs.
MongoDB’s Growth Strategy
- Acquiring New Customers: MongoDB aims to grow its customer base by leveraging word-of-mouth awareness and the popularity of its free offerings. The focus is on enterprises heavily invested in software development, where there’s a substantial need for databases. Direct sales efforts target both domestic and international markets.
- Expanding Sales Within Existing Customers: MongoDB seeks to increase sales within its customer base by offering scalable solutions that align with the growth of customers’ applications. The company aims to standardize its platform within organizations, driving increased usage and subscription expansion.
- Product Innovation: MongoDB continues to invest in product development to expand functionality and address developers’ evolving needs. Recent enhancements include features like column store indexes, in-app analytics, and Atlas Serverless, aimed at enabling developers to handle a wider range of workloads efficiently.
- Fostering Developer Community: MongoDB prioritizes engagement with its developer community, leveraging events, conferences, and educational resources like MongoDB University. Engaged developers often advocate for MongoDB within their organizations, contributing to new customer acquisition and expansion opportunities.
- Partner Ecosystem Growth: MongoDB’s partner ecosystem comprises various technology partners, cloud providers, and systems integrators. Strategic partnerships with major cloud providers like AWS, GCP, and Microsoft Azure enhance joint marketing efforts and provide customers with integrated solutions. Expanding global partnerships, especially in China, aims to drive adoption and market presence.
- International Expansion: MongoDB recognizes significant growth opportunities outside the United States and plans to expand its global footprint. The company intends to continue driving adoption and sales efforts in international markets to capitalize on this potential growth.
Key Highlights:
- Mission and Platform: MongoDB’s mission is to empower developers through software and data. Its integrated developer data platform combines relational and non-relational database strengths, offering performance, scalability, and flexibility.
- Strategic Importance of Database Selection: MongoDB emphasizes the critical role of choosing the right database, directly impacting developer productivity and organizational competitiveness.
- Challenges of Legacy Relational Databases: Legacy relational databases are deemed inadequate for modern software development due to rigidity, lack of cloud support, and scalability issues.
- Generative AI and Database Requirements: The rise of generative AI underscores the necessity for modern databases capable of securely supporting AI-powered applications.
- Additional Platform Capabilities: MongoDB’s platform offers various capabilities like search, vector search, time series, data lifecycle management, and edge computing, providing a comprehensive solution for diverse application needs.
- Market Competitiveness and Growth: MongoDB competes in the fast-growing database management software market, with advancements in coding assistant technology expected to further benefit the market.
- MongoDB Advantage: MongoDB stands out with its developer-centric approach, support for modern applications, and key features like performance, scalability, flexibility, and reliability.
- Support for Any Application Anywhere: MongoDB enables running applications across various environments, offering flexibility and efficiency.
- MongoDB Atlas: MongoDB Atlas simplifies database management by providing MongoDB as a service in the public cloud, allowing developers to focus on application development.
- Key Customer Benefits: MongoDB’s platform maximizes competitive advantage, increases developer productivity, delivers high reliability, reduces complexity, and lowers total cost of ownership for customers.
- Products: MongoDB offers MongoDB Atlas, a managed multi-cloud DBaaS, and MongoDB Enterprise Advanced, a self-managed commercial database offering, along with professional services and free offerings to encourage adoption.
- Growth Strategy: MongoDB’s growth strategy includes acquiring new customers, expanding sales within existing customers, fostering the developer community, growing the partner ecosystem, and expanding internationally. These strategies aim to capitalize on market opportunities and drive customer adoption and retention.
Related Visual Stories
Who Owns MongoDB?
MongoDB Revenue
Is MongoDB Profitable?
Who Owns Oracle
Oracle Business Model
Oracle Revenue
Oracle Profits
Oracle Revenue Breakdown
Oracle Employees
Oracle Revenue Per Employee
The post MongoDB Business Model appeared first on FourWeekMBA.