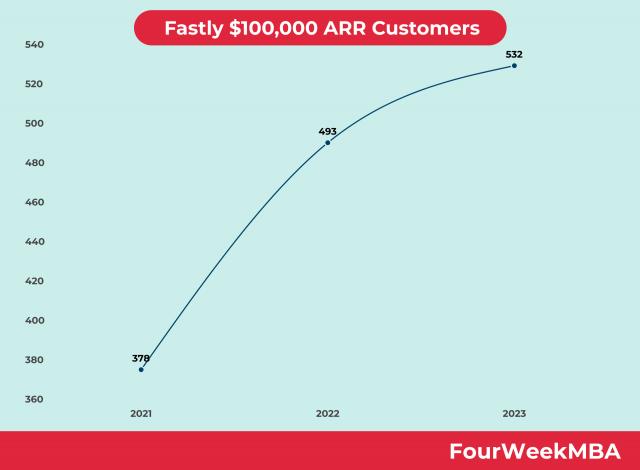
Fastly had 532 $100,000 ARR Customers in 2023, which contributed to most of its revenue, compared to 493 in 2022, and 378 in 2021.
SaaS KPIs and Core Functions
Net Promoter Score
The Net Promoter Score (NPS) is a measure of the ability of a product or service to attract word of mouth advertising. NPS is a crucial part of any marketing strategy, since attracting and then retaining customers means they are more likely to recommend a business to others. Innovation Funnel
An innovation funnel is a tool or process ensuring only the best ideas are executed. In a metaphorical sense, the funnel screens innovative ideas for viability so that only the best products, processes, or business models are launched to the market. An innovation funnel provides a framework for the screening and testing of innovative ideas for viability.
Sales Funnels vs. Flywheels
The sales funnel is a model used in marketing to represent an ideal, potential journey that potential customers go through before becoming actual customers. As a representation, it is also often an approximation, that helps marketing and sales teams structure their processes at scale, thus building repeatable sales and marketing tactics to convert customers.
Engines of Growth
In the Lean Startup, Eric Ries defined the engine of growth as “the mechanism that startups use to achieve sustainable growth.” He described sustainable growth as following a simple rule, “new customers come from the actions of past customers.” The three engines of growth are the sticky engine, the viral engine, and the paid engine. Each of those can be measured and tracked by a few key metrics.
Outside Sales
Outside sales occur when a salesperson meets with prospects or customers in the field. This sort of sales function is critical to acquire larger accounts, like enterprise customers, for which the acquisition process is usually longer, more complex and it requires the understanding of the target organization. Thus the outside sales will cut through the noise to acquire a large enterprise account for the organization.
Inside Sales
Inside sales is the practice of turning leads into customers remotely. Communication between the client and the customer occurs via phone, email, or the internet. Inside sales become a critical sales acquisition strategy when a company or startup needs to convert leads into potential small and medium business paying accounts. Thus, the inside sales representative will help prospect, qualify, assess and close those opportunities.
Freemium Business Model
The freemium – unless the whole organization is aligned around it – is a growth strategy rather than a business model. A free service is provided to a majority of users, while a small percentage of those users convert into paying customers through the sales funnel. Free users will help spread the brand through word of mouth.
Freeterprise Business Model
A freeterprise is a combination of free and enterprise where free professional accounts are driven into the funnel through the free product. As the opportunity is identified the company assigns the free account to a salesperson within the organization (inside sales or fields sales) to convert that into a B2B/enterprise account.
IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS
The “as-a-service” models are typical of the second wave of the Web 2.0, built on top of cloud computing. Indeed, these models’ basic premise is to offer a solution to the final customer without having to host it on-premise, with complex implementations and large overhead. Yet while PaaS and IaaS are skewed toward development teams. SaaS has wider applications toward end-users, also in non-technical departments.
C3.ai Business Model
C3 AI is a cloud-based Enterprise AI SaaS company. It built a set of proprietary applications (known as the C3 AI suite) that offer its clients the ability to integrate digital transformation applications with fast deployment and no overheads. C3 AI makes money primarily via its subscription services and professional fees.
Related Business Model Types
Platform Business Model
A platform business model generates value by enabling interactions between people, groups, and users by leveraging network effects. Platform business models usually comprise two sides: supply and demand. Kicking off the interactions between those two sides is one of the crucial elements for a platform business model success.
Marketplace Business Model
A marketplace is a platform where buyers and sellers interact and transact. The platform acts as a marketplace that will generate revenues in fees from one or all the parties involved in the transaction. Usually, marketplaces can be classified in several ways, like those selling services vs. products or those connecting buyers and sellers at B2B, B2C, or C2C level. And those marketplaces connecting two core players, or more.
Network Effects
A network effect is a phenomenon in which as more people or users join a platform, the more the value of the service offered by the platform improves for those joining afterward.
Asymmetric Business Models
In an asymmetric business model, the organization doesn’t monetize the user directly, but it leverages the data users provide coupled with technology, thus have a key customer pay to sustain the core asset. For example, Google makes money by leveraging users’ data, combined with its algorithms sold to advertisers for visibility.
Attention Merchant Business Model
In an asymmetric business model, the organization doesn’t monetize the user directly, but it leverages the data users provide coupled with technology, thus having a key customer pay to sustain the core asset. For example, Google makes money by leveraging users’ data, combined with its algorithms sold to advertisers for visibility. This is how attention merchants make monetize their business models.
Wholesale Business Model
The wholesale model is a selling model where wholesalers sell their products in bulk to a retailer at a discounted price. The retailer then on-sells the products to consumers at a higher price. In the wholesale model, a wholesaler sells products in bulk to retail outlets for onward sale. Occasionally, the wholesaler sells direct to the consumer, with supermarket giant Costco the most obvious example.
Retail Business Model
A retail business model follows a direct-to-consumer approach, also called B2C, where the company sells directly to final customers a processed/finished product. This implies a business model that is mostly local-based, it carries higher margins, but also higher costs and distribution risks.
B2B2C
A B2B2C is a particular kind of business model where a company, rather than accessing the consumer market directly, it does that via another business. Yet the final consumers will recognize the brand or the service provided by the B2B2C. The company offering the service might gain direct access to consumers over time.
Crowdsourcing Business Model