Context: With COVID-19 pandemic finally waning, the Mrna vaccine developers of the world are left with unsold vaccine shots and idle manufacturing plants.
messenger RNA vaccines:
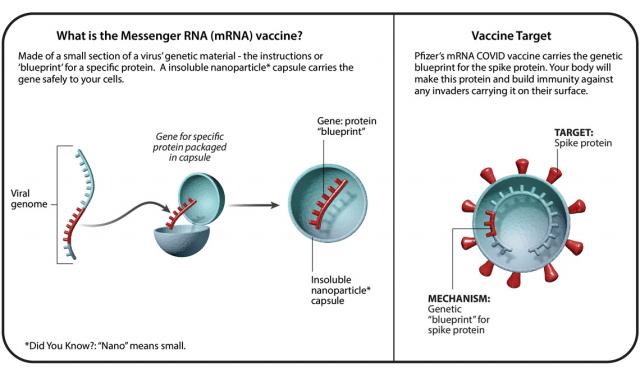
- Most vaccines contain a weakened or dead bacteria or virus. However, scientists have developed a new type of vaccine that uses a molecule called messenger RNA (mRNA) rather than part of an actual bacteria or virus. Messenger RNA is a type of RNA that is necessary for protein production.
- mRNA vaccines are a type of vaccine that uses a small piece of genetic material called messenger RNA (mRNA) to provide instructions to cells in the body. mRNA instructs cells to synthesise specific proteins, which in turn, trigger immune responses.
How do mRNA vaccines work?
- Genetic Sequence Identification: Scientists first identify the genetic sequence of the virus they want to target. In the case of COVID-19, the genetic sequence of the SARS-CoV-2 virus was identified.
- mRNA Production: Using the identified genetic sequence, scientists create a synthetic version of the mRNA that encodes for a specific viral protein, typically the spike protein found on the surface of the virus.
- Vaccine Administration: The mRNA vaccine is administered to individuals through an injection. Once injected, the mRNA enters the cells.
- Cell Translation: Within the cells, the mRNA provides instructions for the production of the viral protein (spike protein in the case of COVID-19). The cells use these instructions to build the protein.
- Immune Response: The spike protein produced by the cells triggers an immune response in the body. The immune system recognises the spike protein as foreign and mounts an immune response to eliminate it.
- Memory Cells: The immune system also creates memory cells that “remember” the spike protein. This way, if the person is later exposed to the actual virus, the immune system can quickly recognize and respond to it, providing protection against the disease.
Advantages of mRNA vaccine:
- No Live Pathogen: Making them safer for individuals with weakened immune systems or other health conditions in comparison to other vaccines.
- Large-scale adaptability and speedy development: Since mRNA vaccines are based on sequences of viral proteins, making a new vaccine could simply involve changing the mRNA sequence if one knows what protein one wants to make.
- Specificity: mRNA vaccines can be designed to target specific antigens, such as viral proteins. This allows for highly targeted immune responses against particular pathogens or diseases.
- Immunological Memory: Once the immune system has encountered the antigen through mRNA introduced by the vaccine, it can respond more rapidly and effectively if exposed to the same antigen in future.
- No Risk of Insertional Mutagenesis as mRNA does not get into the genetic material of the host genome. (Mutagenesis is the creation of mutations in DNA by the addition of one or more base pairs)
Potential Risk:
- They are not as stable at high temperatures, making packaging and distribution difficult. Also, the long-term effects of the vaccines are still unknown.